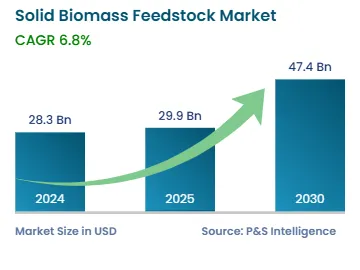
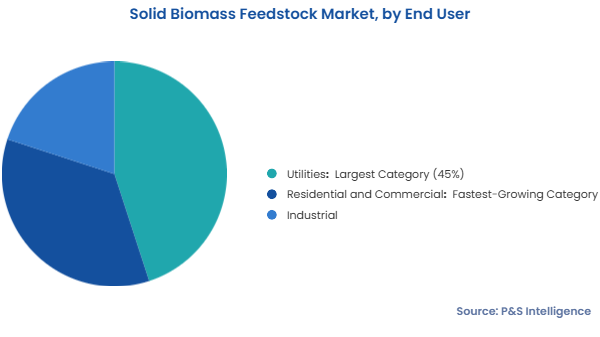
Solid Biomass Feedstock Market Trends and Growth Drivers
Rising Demand for Biofuels Is Key Trend
Biofuels are considered eco-friendly energy resources because they are manufactured from biomass, which can be replenished over time. Government policies are one of the key factors propelling biofuel demand. For instance, the U.S. has implemented the Renewable Fuel Standards (RFS), which mandate that transportation fuel must contain some amount of biofuel.
Biofuels are largely preferred for their ability to lessen greenhouse gas emissions over conventional fossil fuels. This is critical for industries that are harder to decarbonize, including transportation and aviation, where biofuels can offer a cleaner option than gasoline and diesel.
The worldwide drive for energy resilience is developing an interest in easily produced biofuels, which can reduce the dependence on imported petroleum. Biomass feedstock, such as agricultural waste, algae, and manure pellets, can be produced domestically, creating a self-sustained energy supply.
Biofuels are becoming more efficient and economically viable due to the advancements in production technologies. These improvements span various stages of the biofuel production process, from processing methods to conversion technologies, feedstock selection, and scaling up production.
The increasing demand for heat, motive, and electric power continues to widen the range of feedstock used for biofuel production. Consumers widely know of all the pressing environmental issues, which makes the drive toward more sustainable energy sources more imperative.
Increasing Demand for Renewable Energy Is Major Market Driver
The global commitment to reduce carbon release is one of the major drivers for the consumption of biomass. Biomass raw materials, such as agriculture residue, wood pellets, and organic waste, provide a local, renewable energy source, reducing the susceptibilities associated with the variable fossil fuel cost.
Governments across the world are enacting policies and offering financial support to encourage the use of renewable energy, including biomass. The International Renewable Energy Agency (IRENA) says that solid biomass accounted for a global energy production capacity of 103,358 MW in 2023, compared to 100,414 MW in 2022.
Biomass energy is becoming an important part of the renewable energy ecosystem. It is not only used in power plants but also combined heat and power (CHP) systems, where the fuel produces both electricity and heat. Biomass is a versatile choice because it can be used in a wide range of applications, such as , industries, and transportation. The International Energy Agency (IEA) states that biofuel consumption for transportation could increase by 38 billion liters between 2023 and 2028.
The move forward in biomass conversion technologies is helping make it a more-efficient and important energy source. Innovations including torrefaction and gasification are improving the energy conversion efficiency of biomass, making it effortless to store, transport, and use for large-scale power generation.
Biomass energy is frequently seen as eco-friendly alternative, especially when it is obtained from decayed products, such as agricultural and forest leftovers, rather than from crops grown especially for energy. This ensures that the critical food supplies are not affected and the idea of a circular economy can be realized.
High Expenses of Utilizing Solid Biomass Feedstock Present Market Challenges
Pretreatment of solid biomass is a key step in changing the raw material into an intermediate form that can be effectively processed into biofuels or other sources of energy. Every feedstock presents unique challenges, and the need for energy-intensive equipment, costly chemicals, and careful management of byproducts adds further complexity and costs.
Biomass feedstocks are frequently of considerable volumes and have less energy density, making them expensive to transport over long distances. The high transportation expenses can remarkably affect the overall economics of biomass energy production.
The increase in biomass energy production strongly depends on government policies and regulations, such as renewable energy endorsement, carbon credit schemes, and environmental standards. Biomass’s role in minimizing carbon emissions is sometimes questioned, especially if unsustainable sourcing practices are followed.
Dedicated biomass crops often compete with food crops and other land uses, such as forestry and wildlife conservation. This can increase concerns about food security, land degradation, and the displacement of entire communities. These factors can lead to an unwillingness to accept large-scale biomass production and usage.
Biomass also competes with other renewable energy sources, such as solar, wind, and hydropower. As these technologies become more cost-effective and widespread, they could impact the growth of the market for solid biomass feedstock, which is often more costly and less scalable.
Regional Analysis
North America dominates the global solid biomass feedstock market with 40% revenue share in 2024.
In North America, solid biomass feedstock plays a remarkable role in renewable energy production. The region’s vast agricultural and forest assets provide a large variety of biomass materials that are used essentially for bioenergy applications, such as power generation, heating, and transportation. Both the U.S. and Canada have implemented policies to encourage the use of renewable energy, including biomass. Tax credits, renewable energy standards, and green energy programs promote the biomass sector.
The U.S., essentially the southeast, is a prime exporter of wood pellets to Europe, where they are used to meet renewable energy targets. This market has been increasing with pellet production increasingly targeted at European users.
APAC is the fastest-growing regional market. This is because India, China, and several Southeast Asian countries are witnessing rapid growth in industrialization and urbanization. India and China are two of the largest GHG emitters in the world, which is why they are implementing green energy policies and programs to reduce carbon emissions.
India’s National Action Plan on Climate Change (NAPCC) aims to address climate change and promote energy efficiency and renewable energy. Similarly, in 2021, China launched the world’s largest carbon trading market, which initially focuses on the power sector. This market encourages companies to reduce carbon emissions by setting a price on it.
The regions and countries analyzed for this report include:
- North America (Largest Regional Market)
- U.S. (Larger Country Market)
- Canada (Faster-Growing Country Market)
- Europe
- Germany (Largest Country Market)
- U.K. (Fastest-Growing Country Market)
- Italy
- Spain
- France
- Rest of Europe
- Asia-Pacific (APAC) (Fastest-Growing Regional Market)
- China (Largest Country Market)
- India (Fastest-Growing Country Market)
- Japan
- South Korea
- Australia
- Rest of APAC
- Latin America (LATAM)
- Brazil (Largest Country Market)
- Mexico (Fastest-Growing Country Market)
- Rest of LATAM
- Middle East and Africa (MEA)
- U.A.E. (Fastest-Growing Country Market)
- South Africa (Largest Country Market)
- Saudi Arabia
- Rest of MEA